Smart Money Concepts (SMC) have revolutionized the way traders understand market movements, focusing on how institutional players—banks, hedge funds, and liquidity providers—manipulate price action. Unlike traditional retail strategies, SMC leverages liquidity zones, order blocks, and market structure shifts to anticipate high-probability trade setups. But what if you could automate these strategies without any coding? In this guide, we’ll break down the core principles of Smart Money Concepts and show you how to turn them into fully automated trading strategies using an intuitive, no-code platform.
What Are Smart Money Concepts (SMC)
Smart Money Concepts (SMC) have gained significant traction among traders looking to decode the hidden mechanics behind price movements. Unlike retail trading strategies, which often rely on indicators and fixed patterns, SMC focuses on how institutional players—such as banks, hedge funds, and liquidity providers—execute trades. These entities have the capital to influence the market, and they follow structured trading methodologies that revolve around liquidity zones, order blocks, and market structure shifts.
By understanding Smart Money Concepts, traders can stop chasing unreliable setups and instead trade in alignment with the market's actual movers. In this section, we'll explore the role of institutional traders, key principles of SMC, and how it differs from traditional retail trading strategies.
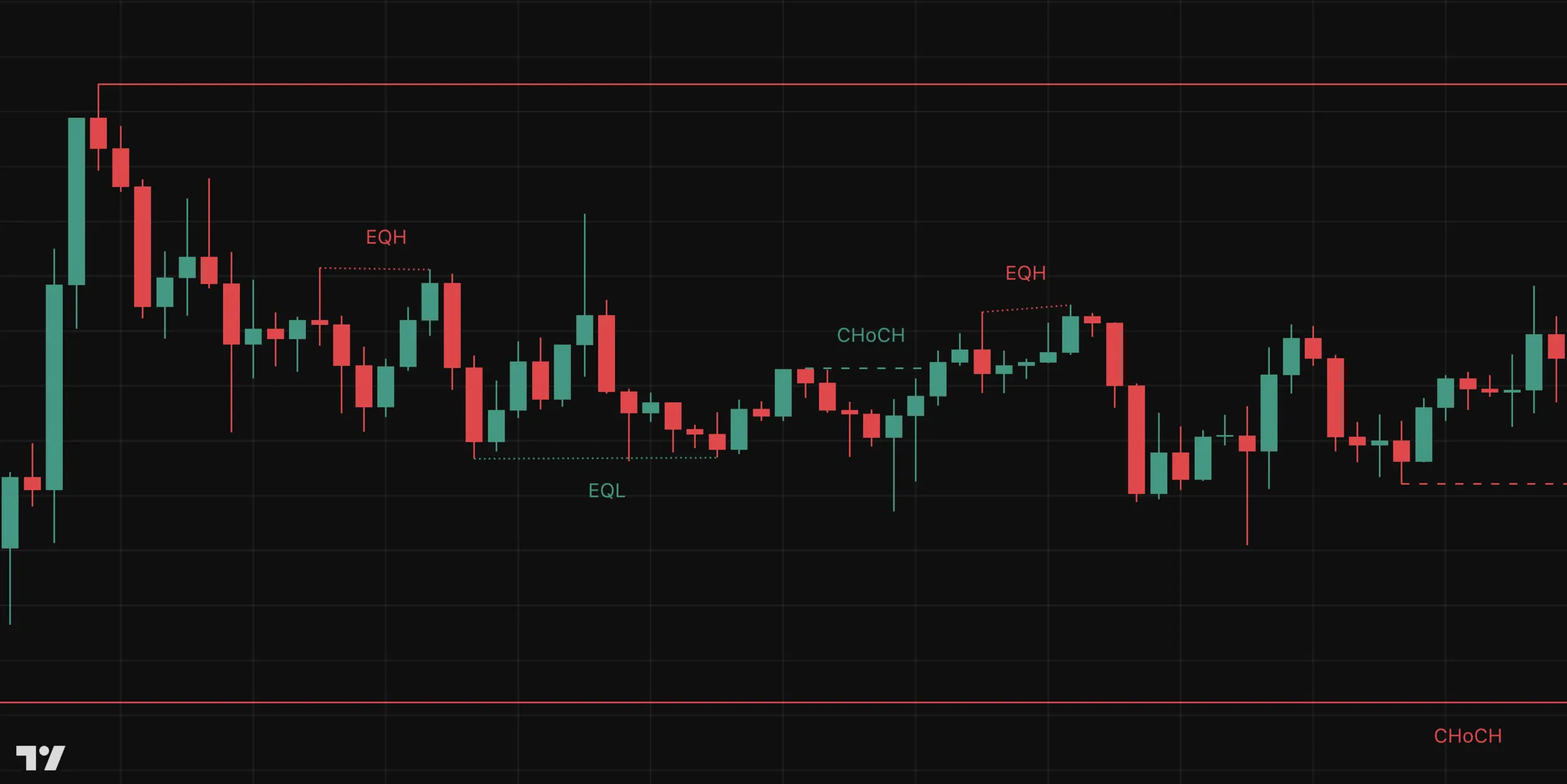
The Role of Institutional Traders in the Market
Retail traders make up a small fraction of market participants, while institutional traders dominate with their large capital, sophisticated algorithms, and advanced risk management strategies. These big players don’t trade based on indicators like RSI or MACD. Instead, they focus on liquidity—identifying where the most buy and sell orders are placed—to create high-probability trade setups.
Institutions frequently execute liquidity grabs (also known as stop hunts), where they push the price in one direction to trigger stop-loss orders before reversing the trend. This manipulation allows them to enter at premium prices while retail traders are left chasing false breakouts.
Understanding how institutions manipulate price movements can help traders align their strategies with these dominant forces rather than being caught on the wrong side of the market.
Key Principles of Smart Money Concepts
SMC is based on price action and the behavior of institutional traders. The core principles include:
- Market Structure Shifts (MSS) and Break of Structure (BOS) – Identifying trend changes based on key support and resistance breakouts.
- Order Blocks – Institutional footprints left behind as large orders are executed.
- Liquidity Grabs – Artificial price movements designed to trigger retail traders’ stop losses.
- Fair Value Gaps (FVG) and Imbalances – Areas where price moves aggressively in one direction, creating inefficiencies that often get filled later.
By mastering these concepts, traders can anticipate where price is likely to move next rather than reacting to lagging indicators.
How SMC Differs from Retail Trading Strategies
Retail trading typically relies on indicators like moving averages, RSI, or Bollinger Bands to generate trade signals. While these tools can be useful, they lag behind price movements and often result in delayed or false signals.
In contrast, Smart Money Concepts rely solely on price action and liquidity analysis, making them more aligned with real market dynamics. Key differences include:
| Aspect | Retail Trading | Smart Money Concepts |
| Decision Basis | Indicators & Patterns | Price Action & Liquidity |
| Entry Strategy | Breakouts, Crossovers | Order Blocks, Liquidity Grabs |
| Stop-Loss Placement | Fixed % or Indicator-Based | Below Liquidity Zones |
| Trading Mindset | Reacting to Trends | Predicting Institutional Moves |
By shifting from a retail trading mindset to an SMC-based approach, traders can improve accuracy and avoid common retail traps.
Core Elements of Smart Money Concepts
Smart Money Concepts revolve around understanding how institutions influence price action and how traders can leverage this knowledge to enter high-probability trades. Unlike traditional trading strategies that depend on indicators, SMC focuses on price movements, liquidity zones, and institutional footprints.
In this section, we’ll break down four key elements of SMC: Market Structure Shifts and Break of Structure (BOS), Order Blocks, Liquidity Grabs, and Fair Value Gaps (FVG). Each of these plays a critical role in identifying institutional activity and improving trade execution.
Market Structure Shifts and Break of Structure (BOS)
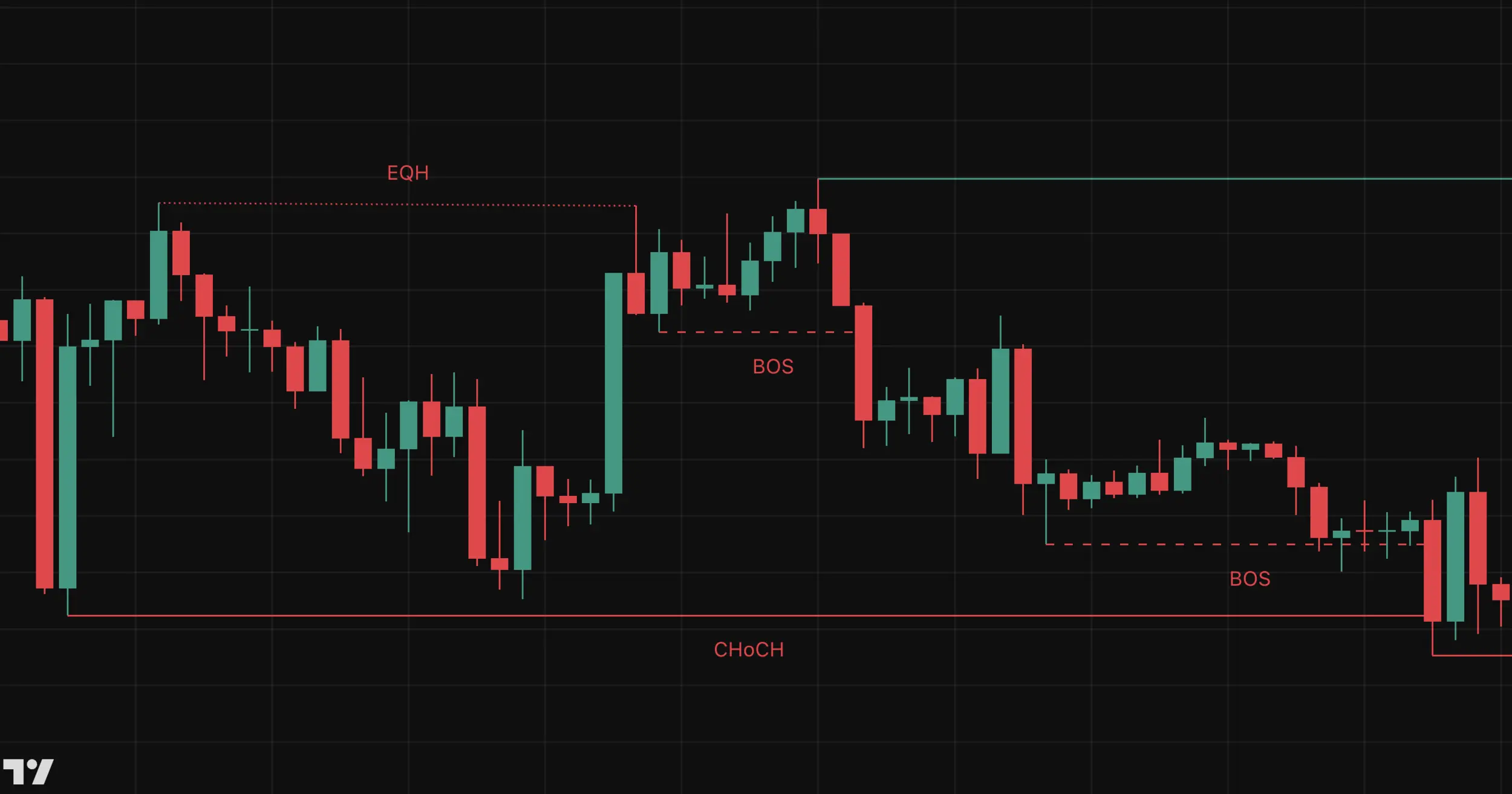
Market structure is the foundation of Smart Money Concepts, dictating whether a market is in an uptrend, downtrend, or range-bound movement. Recognizing market structure shifts allows traders to determine when institutional traders are preparing to reverse or continue a trend.
How Market Structure Works
A trending market follows a series of higher highs (HH) and higher lows (HL) in an uptrend or lower highs (LH) and lower lows (LL) in a downtrend. A trend remains valid until the structure is broken.
A Break of Structure (BOS) occurs when price breaches a significant swing high or swing low, signaling a potential shift in market direction. Institutions use BOS to trap retail traders into thinking the trend will continue, only to reverse shortly after.
Using BOS in Trading:
- In an uptrend, a BOS to the downside suggests institutional selling pressure is increasing.
- In a downtrend, a BOS to the upside indicates potential accumulation before a reversal.
- Traders can enter trades after confirmation of BOS, combined with other SMC elements like order blocks and liquidity grabs.
Example: If BTC/USD is in an uptrend, forming higher highs and higher lows, but suddenly breaks below the most recent higher low, this break of structure (BOS) suggests a potential shift to a downtrend. Traders should wait for confirmation, such as a retest of the broken level, before entering short trades.
Order Blocks: The Footprints of Smart Money
Order blocks are zones where institutions place large buy or sell orders, leaving behind a price footprint. These blocks often serve as areas of support and resistance where price is likely to react.
Types of Order Blocks
- Bullish Order Block (Demand Zone) – A price level where institutions have accumulated buy orders. Price tends to bounce off these areas in an uptrend.
- Bearish Order Block (Supply Zone) – A price level where institutions have placed significant sell orders, causing price to reject upon retesting.
How to Identify Order Blocks
- Look for large candles with strong momentum followed by a pullback.
- The last down candle before a major upward move is a bullish order block.
- The last up candle before a major downward move is a bearish order block.
- Order blocks tend to get respected when price revisits them, making them powerful entry points.
Liquidity Grabs and Stop Hunts
Liquidity is the fuel of the market, and institutions actively seek liquidity zones to execute their large orders efficiently. To do this, they create fake breakouts or stop hunts to trigger retail traders' stop losses before reversing price.
A liquidity grab occurs when price moves aggressively in one direction, takes out stop-loss orders, and then reverses. This is a common institutional tactic used to accumulate or distribute orders.
Types of Liquidity Grabs
- Buy-Side Liquidity Grab – Occurs when price spikes above resistance, triggering stop losses of short traders before reversing downward.
- Sell-Side Liquidity Grab – Happens when price drops below support, triggering stop losses of long traders before reversing upward.
How to Trade Liquidity Grabs
- Look for fake breakouts at key support or resistance levels.
- Wait for price to reclaim the broken level, confirming the trap.
- Combine with order blocks and BOS for stronger confluence.
Example: If ETH/USD has strong resistance at $3,000, and price briefly spikes to $3,020 before dropping back below $3,000, this is a buy-side liquidity grab. Institutions collected liquidity from trapped traders and may now push price lower.
Change of Character (ChoCh)
Change of Character (ChoCh) is a critical concept in Smart Money Concepts (SMC), signaling a potential trend reversal before a full Break of Structure (BOS) occurs. Unlike BOS, which confirms a trend shift, ChoCh acts as an early warning sign, allowing traders to prepare for a possible reversal.
A ChoCh occurs when price behavior deviates from the prevailing trend, often forming a minor break of a previous high or low before a full trend shift. It represents the first sign that institutional traders may be shifting momentum.
ChoCh typically appears when:
- An uptrend forms a lower high (LH) or breaks below a previous higher low (HL) → Bearish ChoCh
- A downtrend forms a higher low (HL) or breaks above a previous lower high (LH) → Bullish ChoCh
This shift suggests that buying or selling pressure is changing, leading to potential reversals.
Key Insight: A ChoCh may turn into a BOS if price continues to break significant swing points.
| Feature | Change of Character (ChoCh) | Break of Structure (BOS) |
| Purpose | Early trend reversal signal | Confirms a trend shift |
| Occurs When | A minor swing high/low is broken | A major swing high/low is broken |
| Strength | Weaker confirmation, but early warning | Strong confirmation of trend change |
| Best Use | Preparing for reversals | Confirming a new trend direction |
Fair Value Gaps (FVG) and Imbalances
Fair Value Gaps (FVG) occur when price moves too fast in one direction, leaving an inefficiency or imbalance in the market. These gaps often get filled later as price retraces to restore equilibrium.
How to Identify Fair Value Gaps
- Look for large, one-sided price movements with minimal pullback.
- FVGs are often found within institutional price movements.
- The middle of an FVG can act as a magnet for price to return and fill the gap.
How to Trade FVGs
- If price leaves a bullish FVG, traders can look for long entries when price revisits the gap.
- If price leaves a bearish FVG, traders can look for short trades when price retraces into the imbalance.
- Combining FVGs with order blocks and BOS improves trade accuracy.
Example: If BTC/USD rallies from $50,000 to $52,000 in a single bullish candle, but leaves a gap between $50,500 and $51,000, this is an FVG. Price may later return to $50,750 (mid-gap) before resuming its trend.
Understanding Market Structure Shifts, Order Blocks, Liquidity Grabs, and Fair Value Gaps gives traders an edge in anticipating institutional movements. Rather than relying on lagging indicators, traders can use these principles to trade in sync with smart money.
In the next section, we'll explore why automating Smart Money Concepts can improve trade execution and remove emotional biases from trading.
Why Automate Smart Money Concepts
Smart Money Concepts (SMC) provide a deep understanding of institutional trading behavior, allowing traders to identify high-probability setups. However, executing these strategies manually can be challenging due to the fast-paced nature of the market, emotional biases, and the need for precision timing. This is where automation comes in—enabling traders to execute SMC-based strategies seamlessly, 24/7, without missing key opportunities.
In this section, we’ll explore the limitations of manual SMC trading, the advantages of automation, and how you can fully automate your SMC-based strategy using a no-code trading platform. Plus, we’ve included a YouTube video tutorial to guide you through the entire process step by step.
The Limitations of Manual SMC Trading
While Smart Money Concepts offer a major edge in trading, applying them manually presents several challenges:
Speed and Precision Are Critical
- Institutional traders move fast, often executing trades in milliseconds.
- Manually identifying Break of Structure (BOS), Change of Character (ChoCh), Order Blocks, and Liquidity Grabs requires constant chart monitoring, making it impractical for most traders.
- Missed entries or late executions can turn a profitable trade into a loss.
Emotional Decision-Making Leads to Mistakes
- Fear and greed often lead traders to exit trades too early or chase price movements.
- Manual execution is prone to hesitation, preventing traders from following their strategy consistently.
- Institutional traders exploit emotional retail traders, often triggering stop losses before moving in the intended direction.
Market Monitoring Is Exhausting
- Markets operate 24/7, especially in crypto, requiring traders to be active at all hours.
- Constant monitoring leads to fatigue and poor decision-making.
- Missing key liquidity grabs or order block retests can mean losing profitable trade setups.
These limitations make manual SMC trading difficult to scale, especially for those looking to trade professionally. The solution? Automating Smart Money Concepts to remove inefficiencies and improve execution.
How to Automate Smart Money Concepts (Full Video Tutorial 🎥)
Automating Smart Money Concepts is now easier than ever with no-code trading automation platforms. You don’t need programming skills to set up and execute SMC-based strategies.
🎥 Watch Our Step-by-Step Guide on Automating Smart Money Concepts
In this video, we’ll cover:
✅ How to detect BOS, ChoCh, and liquidity zones automatically
✅ How to set up entry triggers based on institutional footprints
✅ How to configure stop-loss and take-profit levels for automated execution
✅ How to backtest and optimize your strategy before going live
This guide will show you exactly how to build an automated SMC trading bot that operates in both DEMO and LIVE modes, allowing you to trade like institutions without the stress of manual execution.
Using Multi-Timeframe Analysis to Strengthen SMC Trading
One of the most overlooked yet powerful methods for trading Smart Money Concepts is multi-timeframe analysis (MFT). Institutions don’t make decisions based on a single timeframe; instead, they analyze macro and micro trends before placing trades.
A practical way to use multi-timeframe analysis in SMC trading is:
- Higher Timeframe (1D, 4H): Identify overall market structure, major order blocks, and liquidity pools.
- Mid Timeframe (1H, 30m): Look for Break of Structure (BOS) or Change of Character (ChoCh) to confirm a potential shift.
- Lower Timeframe (15m, 5m): Refine entry and exit points by analyzing order flow and liquidity grabs.
By integrating this approach into an automated trading bot, traders can create dynamic entry conditions based on real institutional activity rather than relying on a single timeframe. This results in higher precision entries and fewer false signals.
Bottom Line: Automate Smart Money Concepts
Smart Money Concepts provide traders with a powerful edge, allowing them to analyze price action the way institutional players do. However, manually executing these strategies comes with challenges like missed opportunities, emotional biases, and the need for constant monitoring. By automating SMC-based trading, you can eliminate human error, execute trades with precision, and trade 24/7 without being glued to the charts.
A trading bot powered by Smart Money Concepts doesn’t just handle trade entries—it also takes care of stop-loss (SL) and take-profit (TP) management, trailing stops, and overall risk control. This ensures that every trade is executed according to predefined rules, maintaining a structured risk management approach while allowing for consistent strategy execution.
If you're ready to trade like institutions without the stress of manual execution, automation is the way forward. Watch our full video tutorial to see how you can set up an SMC-powered trading bot today and start taking advantage of institutional strategies—without needing to code. 🚀